The Compressed Work Week – Advantages and Disadvantages


In a compressed work week, a 40-hour week is compressed into fewer days, usually four instead of the regular five.
Compressed work week arrangements can provide a simple solution for balancing high workload periods when they occur in a company.
In this post, we will take a closer look at the compressed work week, often also referred to as the compressed schedule, its structure, advantages, and disadvantages.
What is a compressed work week? How is it different from other types of flexible work policies?
A compressed work week is one option when implementing a flexible work policy. It allows employees to work full-time hours (40 hours per week) over fewer days.
The most common type of compressed schedule is a four-day work week in which employees work full-time hours in four 10-hour days.
Another popular model of the compressed work week is the 5-4-9 work schedule, which is based on the two-week working period.
An employee works 9 hours per day, but then in the second week takes the Friday off. Basically, in two work weeks an employee works 9 days for 9 hours.
This allows employees to work longer hours on some days and accrue enough time for an additional day off.
The main idea of the compressed work week is for employees to have another day off, and it can also be beneficial for companies balancing high workloads.
The compressed work week is most popular in the following industries:
- Forestry and mining
- Utilities
- Manufacturing
- Education and health care services
- Retail
The compressed work week is just one among many different possible flexible work policies, such as:
- Remote work – working from a different location than official offices
- Job sharing – two or more employees sharing the same job
- Part-time work – working fewer hours per week than the typical 40 for a specific job
- Flexitime – keeping flexible when employees work during the day
Advantages and disadvantages of a compressed work week
Below we’ve listed the main advantages and disadvantages of a compressed work week:
Advantages
- An additional day off affords employees a better work/life balance
- The employee keeps full pay and benefits
- Reduced commuting time and costs
- Fewer interruptions and higher productivity in non-regular office hours
- Increase in total staff hours during high peak workloads by overlapping schedules
- Extended hours of workplace operation
- Managing excessive accrued time
Disadvantages
- Some positions may not be suitable for longer hours because of an increased risk of injury or errors
- Less supervision in some time periods
- Could cause understaffing in some time periods
- May create difficulties in scheduling meetings
- Employees could be working unauthorized overtime
- A longer schedule could cause lower productivity at the end of the day
Did we forget anything? Let us know if you have any experience with compressed work weeks.
What to consider when implementing a compressed work week
When creating your flexible work policy, you should definitely take the compressed work week into consideration. A compressed schedule is highly beneficial for both parties.
It provides employees with larger blocks of time off while at the same time extending the operational hours of the company.
You can track employee productivity at the start of the arrangement to make sure there is no decrease, and like many other employers, you could even find it increasing.
Following these measures means you shouldn’t run into any difficulties:
- Set the core office hours, during which employees are required at the office, to avoid understaffing and scheduling issues.
- Provide your employees with enough breaks to keep them focused and motivated.
- Choose a tool for recording employee attendance to monitor the total hours worked and overtime.
Other questions to consider when implementing compressed work week:
- Is the work load on the extended-hour days still healthy?
- Can employees cover each other’s work on off days?
- Will there be any issues with meeting customer demands?
- Is a compressed work week the right arrangement for each specific employee?
- Will there be any problems with staff meetings, where everyone must be present?
- Will there be any problems resulting from fewer interactions among employees?
- Will the productivity of the organization be increased or decreased?
When setting the compressed work week rules, you also have to be careful not to exceed the legal limit of how many hours an employee can work per week.
Countries have different daily maximums, but most often they are in the 9 – 13 hours per day range.
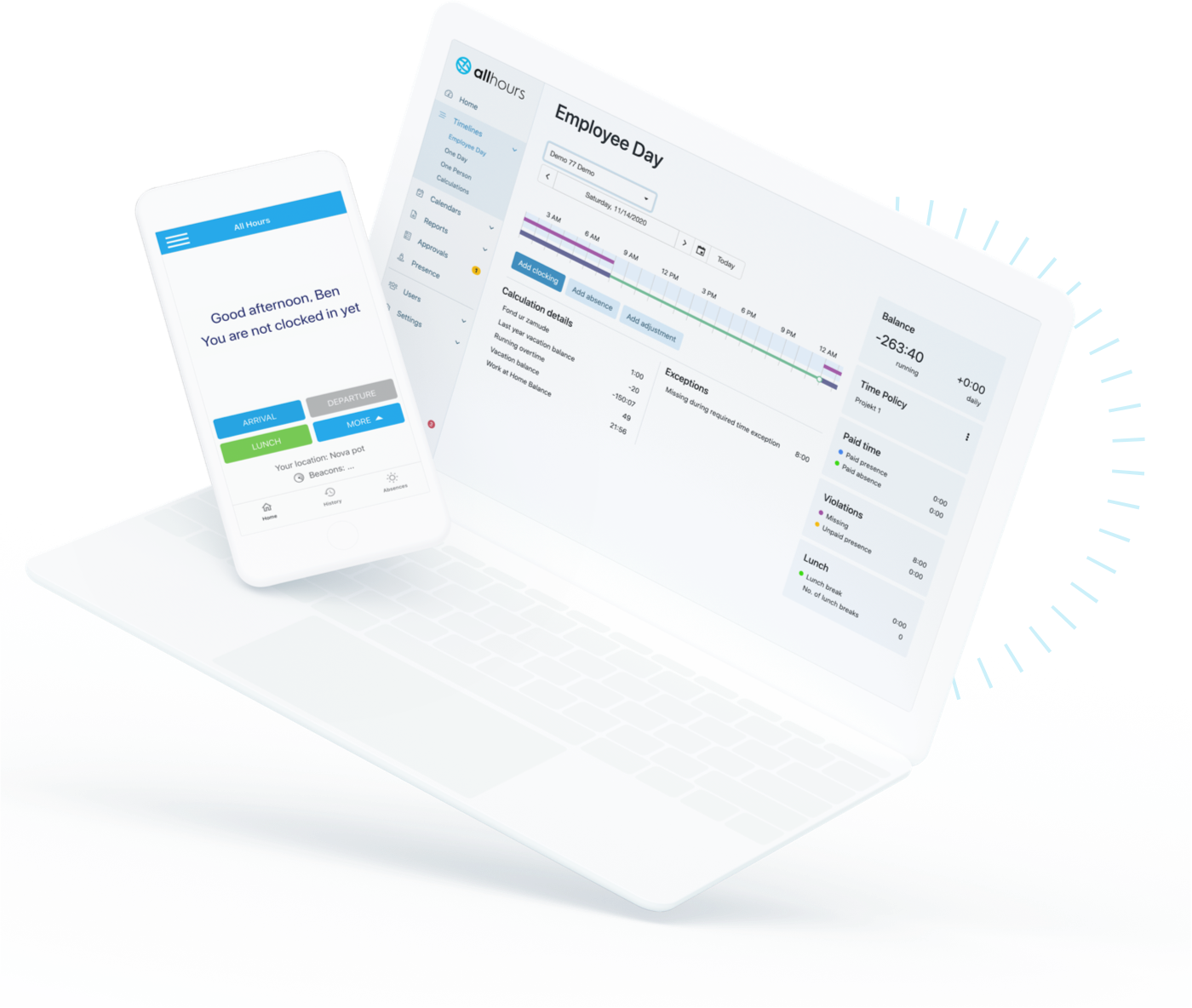
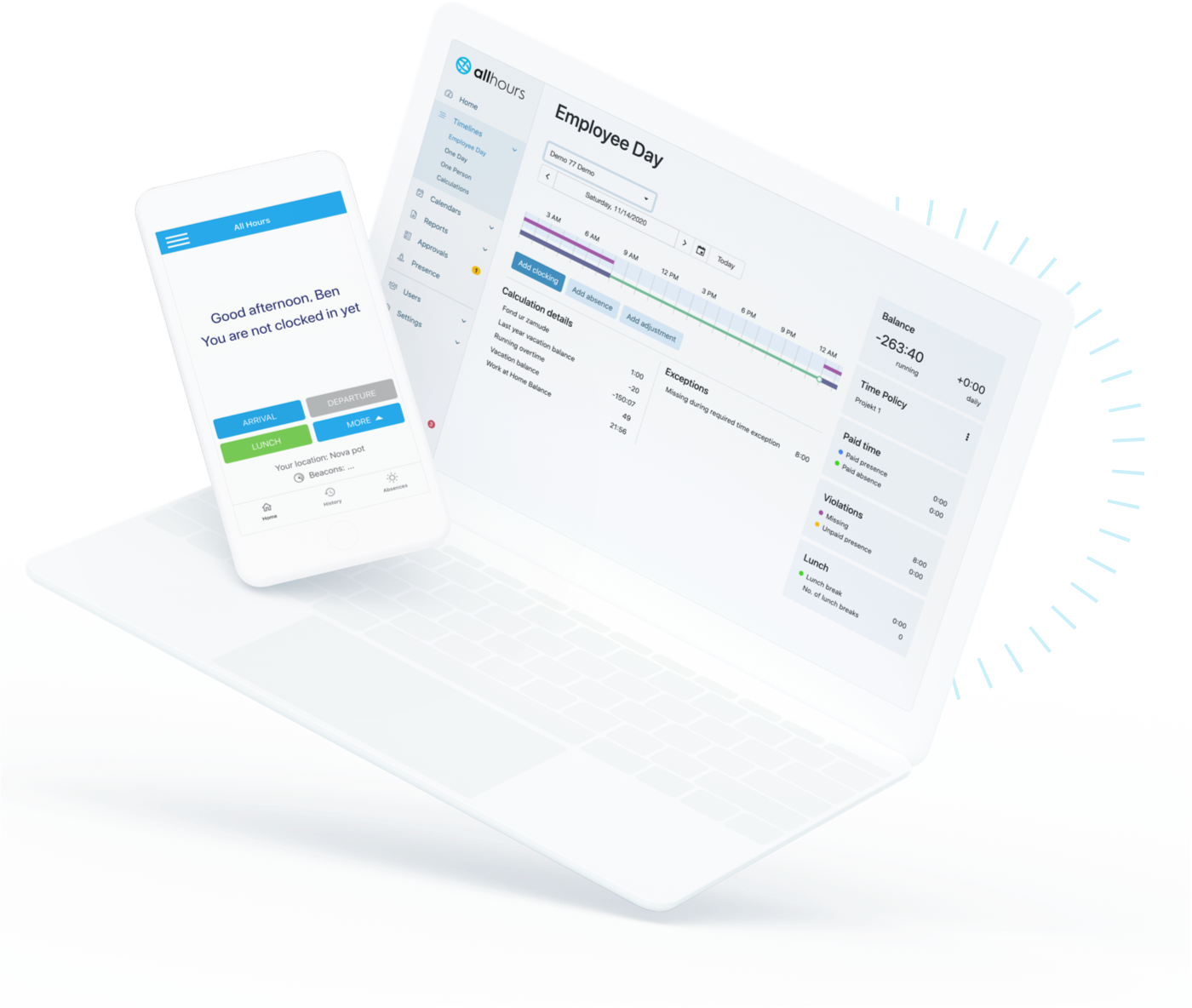
How to set compressed work week in All Hours
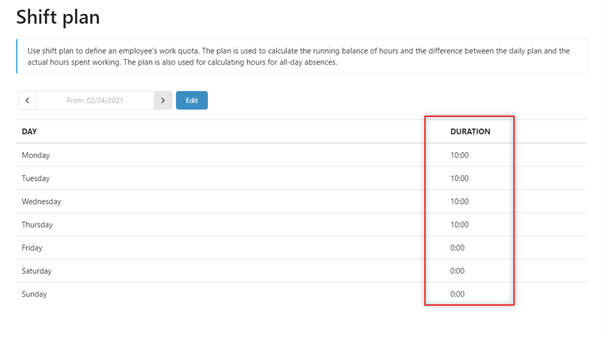
1. Set the ‘Shift Plan’ rule to 10 hours from Monday to Thursday and 0 hours on Friday to define the Monday to Thursday compressed work week.
2. Set the ‘Shift Start’ to 8 AM for each day. The rules below will be applied at the start of the shift.
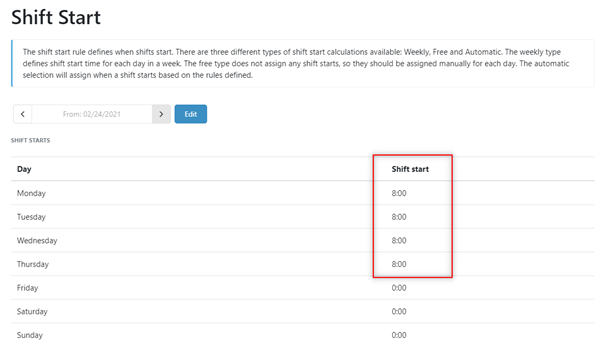
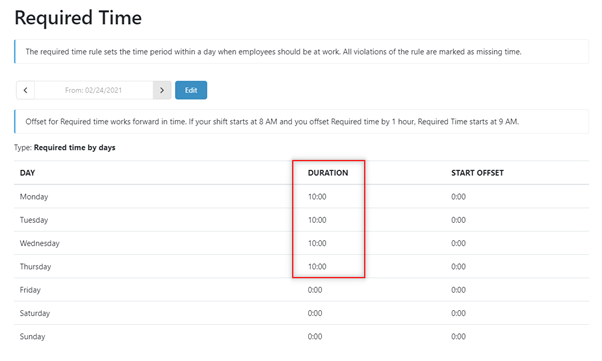
3. Set the ‘Required Time’ rule for the time when the employee is required to be present at the office. In this case, this Is for 10 hours per day from Monday to Thursday, starting at 8:00 AM.
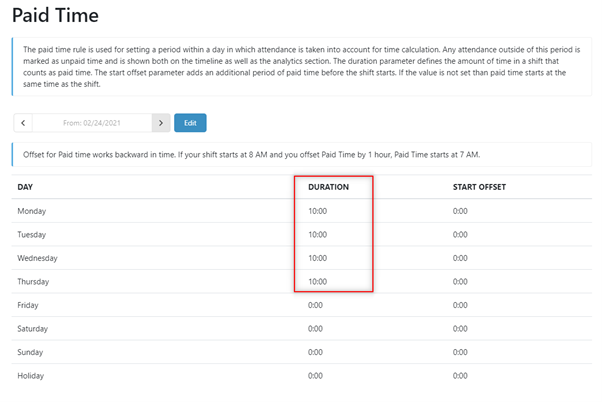
4. Set the ‘Paid Time’ rule for the time in which worked hours will be taken into account as paid time. In this case, this is from 8:00 AM to 6:00 PM, Monday to Thursday so 10 hours on each of these days:
Track your compressed work hours with All Hours. Try it out for free, all features included.